It is done during emergencies where patient is suffering from low heart rates due to various conditions. This is either done from the right femoral vein (Right Groin) or from the right Jugular Vein (Right neck), under local anaesthesia. It’s a single chamber pacemaker which is operated from outside the body by doctors. If patient doesn’t get back to his normal heart rate or rhythm in a couple of days, permanent pacemaker would be a choice of further management.

When the need for TPI is over, it is taken out from the body & if PPI (Permenant Pacemaker Implantation) is required, a PPI is implanted and TPI is removed.
A pacemaker is implanted to help control your heartbeat. Your doctor may recommend a temporary pacemaker when you have a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) after a heart attack, surgery or medication overdose but your heartbeat is otherwise expected to recover. A pacemaker may be implanted permanently to correct a chronic slow or irregular heartbeat or to help treat heart failure.

The heart's conduction systemOpen pop-up dialog box
The heart is a muscular, fist-sized pump with four chambers, two on the left side and two on the right. The upper chambers (right and left atria) and the lower chambers (right and left ventricles) work with your heart's electrical system to keep your heart beating at an appropriate rate — usually 60 to 100 beats a minute for adults at rest.
Your heart's electrical system controls your heartbeat, beginning in a group of cells at the top of the heart (sinus node) and spreading to the bottom, causing it to contract and pump blood. Aging, heart muscle damage from a heart attack, some medications and certain genetic conditions can cause an irregular heart rhythm.
Pacemakers work only when needed. If your heartbeat is too slow (bradycardia), the pacemaker sends electrical signals to your heart to correct the beat.
Some newer pacemakers also have sensors that detect body motion or breathing rate and signal the devices to increase heart rate during exercise, as needed.
Complications related to pacemaker surgery or having a pacemaker are uncommon, but could include:
It is done under local anaesthesia, generally can take upto 2-3 hours. However, the amount of sedation needed for the procedure depends on your specific health conditions. You may be fully awake or lightly sedated
A specialist will insert an IV into your forearm or hand and give you a medication called a sedative to help you relax. Your chest is cleaned with special soap.
However, the amount of sedation needed for the procedure depends on your specific health conditions. You may be fully awake or lightly sedated
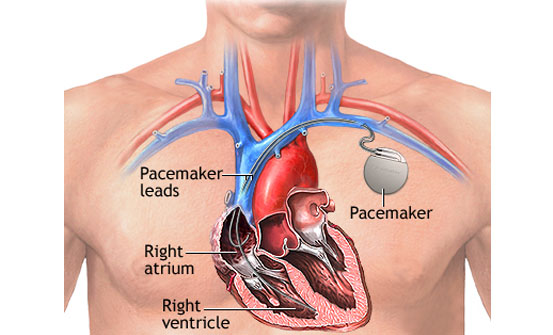
one lead inserted in the right atrium and another lead in right ventricle-Total 2 leads
One or more wires are inserted into a major vein under or near your collarbone and guided to your heart using X-ray images. One end of each wire is secured at the appropriate position in your heart, while the other end is attached to the pulse generator, which is usually implanted under the skin beneath your collarbone.
You will be in the ICU for 24 hours for observation and two days in the ward
Your Pacemaker device will be interrogated again before discharged by the company person
You are restricted for the hand movement for 48 hours and then physiotherapy is started
It's unlikely that your pacemaker would stop working properly because of electrical interference. Still, you'll need to take a few precautions:
Devices that are unlikely to interfere with your pacemaker include microwave ovens, televisions and remote controls, radios, toasters, electric blankets, electric shavers, and electric drills.